Electromagnetic Phenomena in Technology
- Get link
- Other Apps
Electromagnetic Phenomena in Technology: Harnessing the Power of Waves
Introduction:
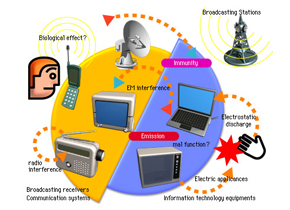
Electromagnetic phenomena are at the core of many technological marvels that shape our modern world. From communication and transportation to computing and energy generation, electromagnetic waves play a crucial role in various technological applications. In this article, we will explore the diverse uses of electromagnetic phenomena in technology and how they have revolutionized different industries.
1. Communication Technology:
One of the most significant applications of electromagnetic phenomena is in communication technology. Electromagnetic waves are the foundation of wireless communication, enabling the transmission of data, voice, and video across vast distances. Let's delve into some key communication technologies:
a. Radio Communication: Radio waves, a type of electromagnetic wave, are used for terrestrial and satellite-based radio communication. Radio waves allow us to broadcast music, news, and other information to a wide audience. They are also utilized in two-way communication systems like walkie-talkies and mobile phones.
b. Television Broadcasting: Electromagnetic waves, primarily in the radio frequency spectrum, facilitate television broadcasting. TV stations transmit audio and video signals over the airwaves, allowing viewers to receive and watch programs on their television sets.
c. Satellite Communication: Satellites in space use electromagnetic waves to relay signals for various purposes, including television broadcasting, weather monitoring, global positioning systems (GPS), and long-distance communication. Satellite communication facilitates global connectivity and enables real-time information exchange.
d. Cellular Communication: Cellular networks rely on electromagnetic waves to enable mobile communication. Mobile phones use radio waves to transmit voice and data signals to nearby cell towers, which then route the signals to their intended destinations.
2. Computing and Information Technology:
Electromagnetic phenomena are also instrumental in computing and information technology, facilitating data transmission, processing, and storage.
a. Fiber Optics: Fiber optic cables use pulses of light (electromagnetic waves in the visible spectrum) to transmit data at incredibly high speeds over long distances. This technology has revolutionized data communication, allowing for faster internet connections and efficient networking between computers and data centers.
b. Wireless Data Transmission: Wi-Fi and Bluetooth technologies rely on electromagnetic waves to enable wireless data transmission between devices such as laptops, smartphones, and IoT devices. These technologies have untethered our devices, making communication and data exchange more convenient.
c. Magnetic Storage: Hard disk drives and magnetic tape storage systems utilize electromagnetic phenomena to read and write data using magnetic fields. This technology provides a cost-effective and efficient way to store large amounts of data in various devices.
3. Transportation and Navigation:
Electromagnetic phenomena have transformed transportation and navigation systems, enhancing safety and efficiency in various ways.
a. Global Positioning System (GPS): The GPS system relies on a network of satellites that use electromagnetic waves to provide precise location and navigation information to GPS receivers on the ground. This technology revolutionized navigation, making it possible to pinpoint locations with high accuracy and enabling applications such as mapping and location-based services.
b. Radar Systems: Radar technology uses electromagnetic waves, usually in the microwave range, to detect and track objects such as aircraft, ships, and weather patterns. Radar plays a crucial role in aviation, maritime navigation, weather forecasting, and military applications.
4. Energy Generation and Transmission:
Electromagnetic phenomena are essential in both traditional and renewable energy generation and transmission.
a. Electromagnetic Induction: Electromagnetic induction is the principle behind electrical power generation in traditional power plants. By rotating a coil of wire in a magnetic field, an electrical current is induced, generating the electricity that powers our homes and industries.
b. Transformers: Transformers use electromagnetic induction to step up or step down voltage in power transmission and distribution systems. These devices enable efficient electricity transmission over long distances and voltage adjustment for various end-use applications.
c. Solar Energy: Photovoltaic cells, commonly known as solar panels, convert sunlight (electromagnetic waves) into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Solar energy is a clean and renewable source of power, and its utilization is growing rapidly.
Conclusion:
Electromagnetic phenomena are ubiquitous in modern technology, playing a vital role in communication, computing, transportation, energy, and numerous other fields. From wireless communication to fiber optics, from GPS to radar systems, and from electrical power generation to solar energy, electromagnetic waves have revolutionized the way we live and interact with our world. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further innovations and applications harnessing the power of electromagnetic phenomena, driving progress and shaping the future.
- Get link
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment